4 D printing: future technology.
What is 4D printing?
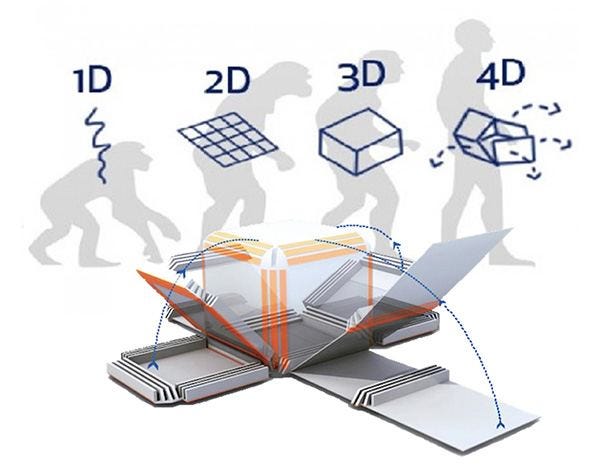
4-dimensional printing also known as 4D bioprinting, active origami, or shape transformation systems) uses the same 3D printing techniques through the computer-programmed deposition of material in successive layers to create a three-dimensional object. However, 4D printing adds the dimension of transformation over time. Therefore, it is a type of programmable matter, in which after the manufacturing process, the printed product reacts with parameters within the environment (humidity, temperature, etc.) and changes its shape accordingly. The ability to do so arises from nearly infinite configurations at micrometer resolution, creating solids with engineered molecular spatial distributions and therefore enabling unprecedented multifunctional performance. 4D printing is a relatively new advance in biofabrication technology, rapidly emerging as a new paradigm in disciplines such as bioengineering, materials science, chemistry, and computer science.
4D printing, like 3D printing, is a process in which material is applied by layer and three-dimensional objects (parts) are generated, but the fourth dimension, time, is also considered here for finished parts. As a result, objects can move and / or change under a certain sensory trigger, such as when in contact with water, heat, vibration, or sound (smart stuff). 4D printing is in an early stage of development and combines various sciences such as bioengineering, materials science and engineering, chemistry, and computer science and engineering.
Hypothetical applications
Possible conceivable application areas are:
- Home and garden (eg, automatic furniture construction, lawn field adaptation)
- Building safety, architecture, environmental protection and energy technology (eg self-regenerating pipes)
- Garment and textile industry (eg , for climate adaptation)
- Aerospace engineering, transportation and traffic engineering (e.g. adaptation of material to environmental conditions, shape-shifting spacesuit, self-build barriers)
- Medical technology and biology (e.g. growing implants, bioprinters)
Printing techniques

Stereolithography is a technique that uses 3D printing photopolymerization to bond the substrate to be placed layer upon layer, creating a polymer network. Unlike fused deposition models, where the extruded material immediately hardens to form layers, 4D printing relies primarily on stereolithography, where in most cases UV light is used to cure the layered materials once finished the printing process. Anisotropy is vital in engineering the direction and magnitude of transformations in a given condition, arranging micro-materials so that there is directionality embedded in the finished print.
Pattern-based 4D printing

It is possible, through 4D printing, to achieve fast and precise manufacturing methods to control the spatial performance of autoflexion in custom designed soft structures. Spatial and temporal transformations can be performed through various trigger mechanisms, such as liquid crystal gel phase transition, coefficient of thermal expansion, discrepancies in thermal conductivity, and different swelling and swelling ratios of the beams. two-layer or composite. One approach to modeling 4D printing is to control 3D printing parameters, such as different spatial patterns of hinges that affect the response time and bending angle of 4D printing products. For it, A parametric model was developed of the physical properties of shape memory polymer panels incorporating 3D printed patterns. The proposed model predicts the final shape of the actuator with excellent qualitative agreement with experimental studies. These validated results can guide the design of functional, pattern-based 4D prints.
Rebel Science Society for Science Physics future
https://instagram.com/science._.journal?utm_medium=copy_link
